RECOGNITION AND ASSESSMENT
Symptoms and signs
- >1 watery, loose or unformed stools within 24 hr
- ± signs of colitis
RISK FACTORS
- Recent or current IV or oral broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment
- Gastric acid suppression
- Advanced age
- Prior hospitalisation
- Duration of hospitalisation
- Care home residency
- Abdominal surgery
- NG tube
INITIAL MANAGEMENT
Laxative or antibiotic treatment
- If the diarrhoea may be caused by laxative or antibiotic
- stop laxative and, if possible, stop antibiotics
- for 24 hr follow impact on diarrhoea
- If the diarrhoea stops, do not submit a stool sample
- If the diarrhoea continues, send diarrhoeal stool sample
New unexplained diarrhoea
- Isolate patient with in a side room (any ward) within 2 hr
- Send diarrhoeal stool sample with clinical information as soon as possible
- If no side room available on ward, promptly escalate to site manager
INVESTIGATIONS
- FBC for WBC↑
- U&E
Stool sample for microbiology
- Diarrhoeal sample is a stool taking the shape of the container
- Laboratory will not test formed stool for evidence of CDI, and will not test a repeat diarrhoeal sample within 28 days of a positive C. difficile toxin EIA stool test result
- Interpretation provided with all test reports:
- C. difficile GDH antigen screening test (GDHA)
- C. difficile toxin EIA test (TEIA)
- if GDHA and TEIA results are both concordant positive or negative, then these results are reported as final without further tests for CDI
- if GDHA and TEIA are both negative, consider alternative diagnosis and do not send repeat sample within 72 hr
- if GDHA and TEIA are both positive, then this supports a diagnosis of CDI since C. difficile toxin itself has been detected
- if GDHA and TEIA discordant, then a PCR assay for C. difficile toxin B gene (PCRT) and C. difficile binary toxin gene (PCRB) is performed on same or next day to clarify the discordant GDHA and TEIA test results
- if positive GDHA screening test with negative TEIA, PCRT and PCRB test results, consider alternative diagnosis since no toxigenic C. difficile detected
- do not send repeat sample within 72 hr
- if diarrhoea continues and no alternative diagnosis for diarrhoea found,
send diarrhoeal sample after 72 hr
- if positive GDHA, negative TEIA, and positive PCRT or positive PCRB, consider symptoms/signs and other results to distinguish between patient with CDI and patient who is a carrier of toxigenic C. difficile with diarrhoea by alternate cause [infectious (e.g. Norovirus, Campylobacter) or non-infectious, e.g. inflammation, drug-induced]. If diarrhoea continues in the absence of alternative diagnosis, then this supports a diagnosis of CDI even though production of C. difficile toxin is below detection level of the toxin EIA assay
- do not send repeat sample within 72 hr
Colitis
- Signs of colitis: X-rays/CT scan abdomen
- Lower gastrointestinal endoscopy for tissue biopsy
- invasive
- severe colitis may increase risk of perforation (if perforation suspected/imminent contact general surgeon)
- In case of doubt about diagnosis, contact gastroenterologist for advice and endoscopy
CONFIRMED CDI MANAGEMENT
- Confirmed=Stool C. difficile GDHA positive with TEIA, PCRT or PCRB positive
Management
- Nurse in single room (any ward)/C. difficile cohort ward
- Contact infection prevention team (IPT)
- Avoid successive uninterrupted courses of different antimicrobials for any indication
TREATMENT
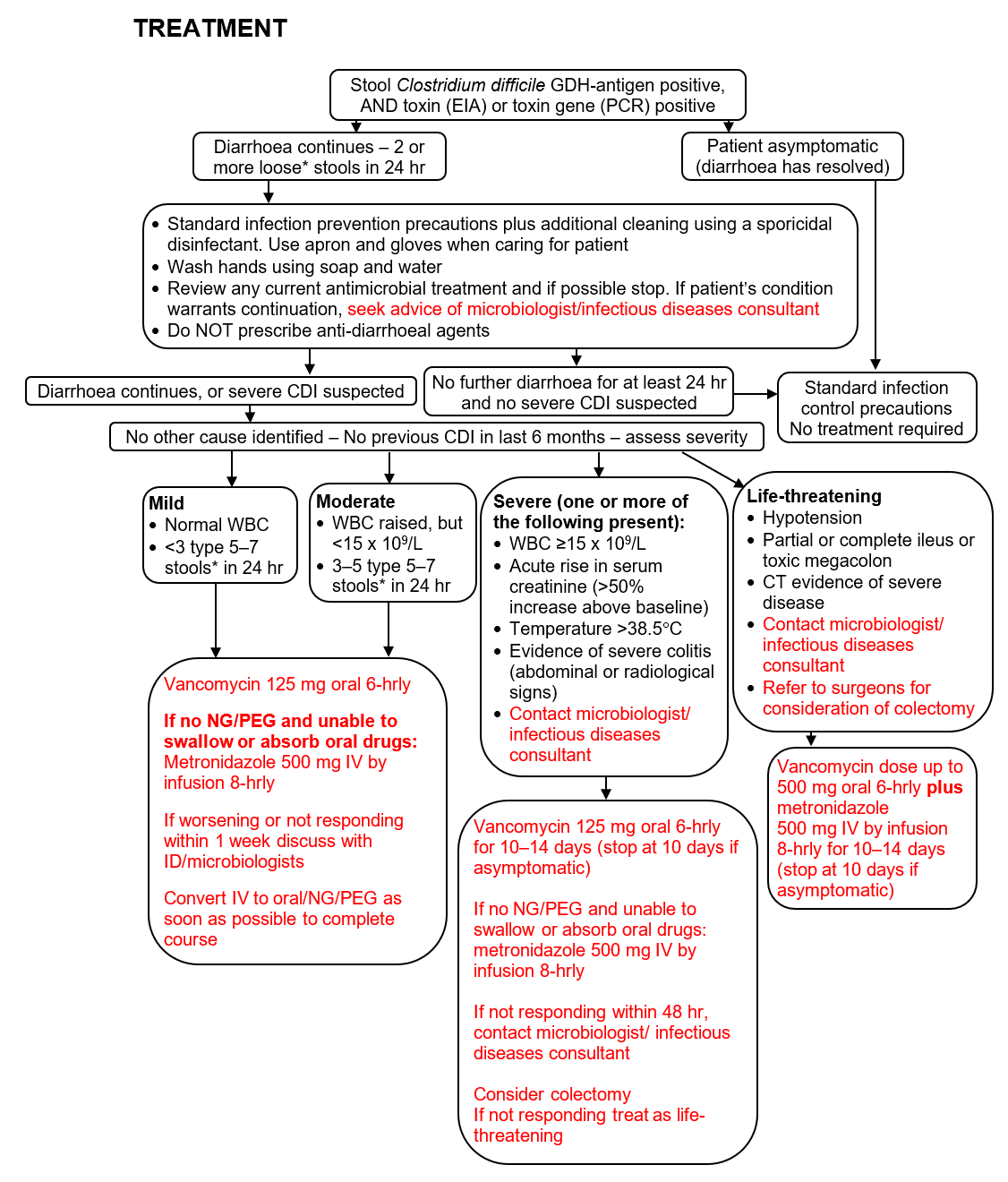
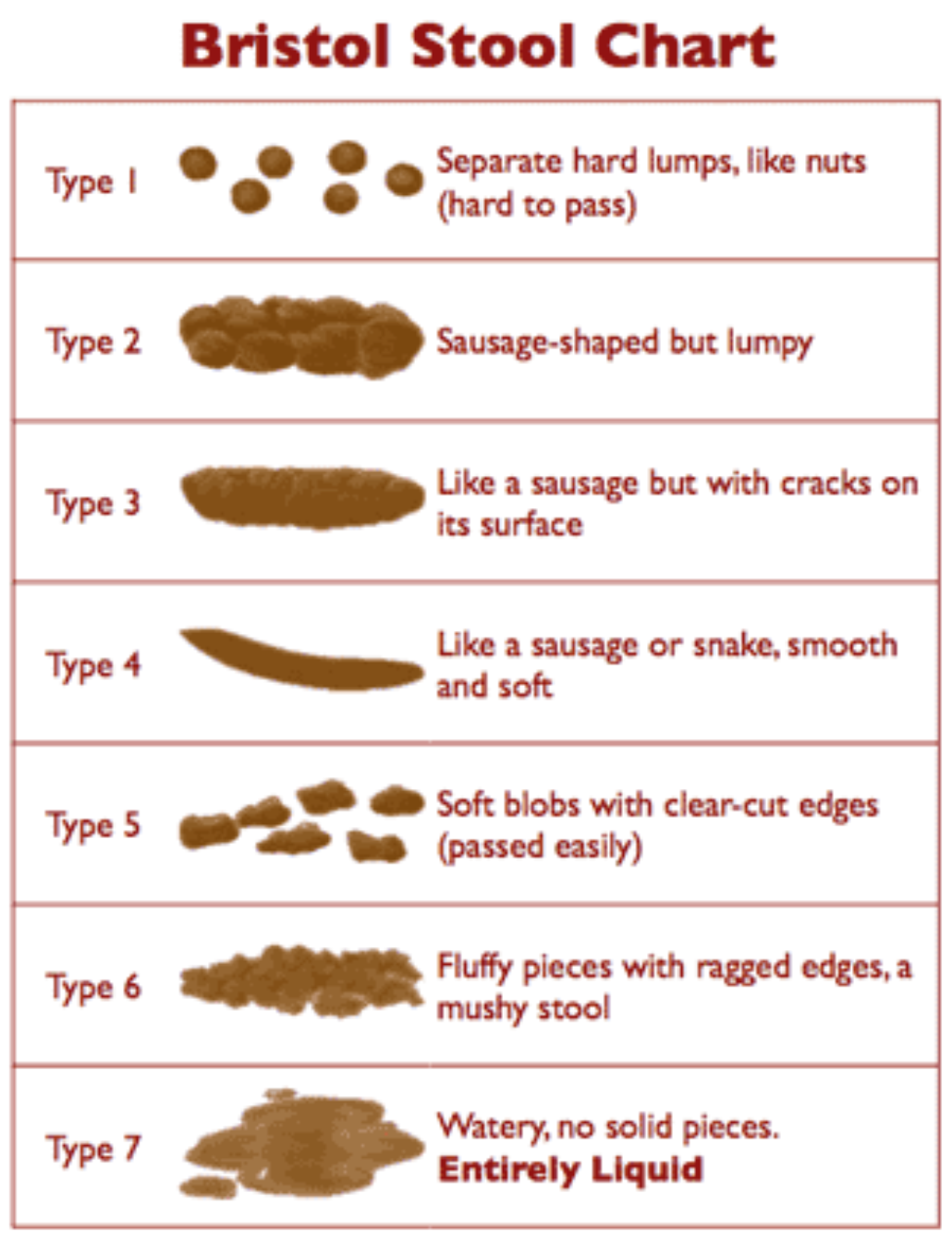
SUBSEQUENT MANAGEMENT
- Nurse patient in side room/cohort ward until symptom-free for 72 hr
- If another cause identified, discuss with microbiologist/ID consultant
- If mild/moderate CDI deteriorates, or if diarrhoea fails to respond to antimicrobial treatment of CDI for>5 days, discuss with microbiologist/ ID consultant
Repeat stool samples
- Unless diagnosis in doubt, do not send repeat stool within 72 hr
- If GDHA and TEIA positive, do not send further stool for CDI testing within 28 days
- stool can remain toxin positive for several weeks
RECURRENCE/NON-RESPONDER
- Keep in side-room irrespective of symptoms until the first of:
- hospital discharge or
- 6 months have elapsed since last CDI diagnosis
- Review any current antimicrobial treatment and if possible, stop
- If life-threatening colitis, refer to GI surgeons for consideration of colectomy
- Contact microbiologists for advice which may include:
- first recurrence within 6 months, or if no response to oral vancomycin within 2-5 days, treat with fidaxomicin 200 mg 12-hrly for 10 days
- subsequent recurrence within 6 months (3rd or further episode of CDI), consider FMT (see below) or commence fidaxomicin 200 mg 12-hrly, to be given for 10 days
Faecal microbiota transplant (FMT) infusion
- Infusion of a filtrate of gut flora derived from healthy donor faeces
- Patients with recurrent CDI treated with FMT demonstrated:
- 91% primary cure rate with symptoms usually resolving within 48 hr
- reduced risk of recurrent CDI in the following months provided that the patient does not receive further antibiotics
- Consider FMT for a 3rd or further episode of CDI
Administration
- Obtain patient’s consent
- Contact microbiologist
- Complete FMT order form for microbiologist to order from the local PHE Laboratory
- Preparation of stool from pre-screened universal donors will arrive in 3-4 days
- Stop all antibiotic treatment (including for CDI) on the day before FMT is to be administered
- Prepare patient for administration
- via nasogastric, naso-jejunal tube or PEG
- if above routes are not an option, via colonic infusion by a gastroenterologist
Last reviewed: 2025-10-23